 #
#
Suitability of Laurentian Great Lakes for invasive species based on global species distribution models and local habitat
Abstract
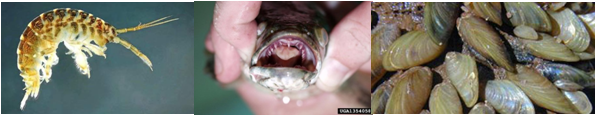
Efficient management and prevention of species invasions requires accurate prediction of where species of concern can arrive and persist. Species distribution models provide one way to identify potentially suitable habitat by developing the relationship between climate variables and species occurrence data. However, these models when applied to freshwater invasions are complicated by two factors. The first is that the range expansions that typically occur as part of the invasion process violate standard species distribution model assumptions of data stationarity. Second, predicting potential range of freshwater aquatic species is complicated by the reliance on terrestrial climate measurements to develop occurrence relationships for species that occur in aquatic environments. To overcome these obstacles, we combined a recently developed algorithm for species distribution modeling—range bagging—with newly available aquatic habitat-specific information from the North American Great Lakes region to predict suitable habitat for three potential invasive species: golden mussel, killer shrimp, and northern snakehead. Range bagging may more accurately predict relative suitability than other methods because it focuses on the limits of the species environmental tolerances rather than central tendency or “typical” cases. Overlaying the species distribution model output with aquatic habitat-specific data then allowed for more specific predictions of areas with high suitability. Our results indicate there is suitable habitat for northern snakehead in the Great Lakes, particularly shallow coastal habitats in the lower four Great Lakes where literature suggests they will favor areas of wetland and submerged aquatic vegetation. These coastal areas also offer the highest suitability for golden mussel, but our models suggest they are marginal habitats. Globally, the Great Lakes provide the closest match to the currently invaded range of killer shrimp, but they appear to pose an intermediate risk to the region. Range bagging provided reliable predictions when assessed either by a standard test set or by tests for spatial transferability, with golden mussel being the most difficult to accurately predict. Our approach illustrates the strength of combining multiple sources of data, while reiterating the need for increased measurement of freshwater habitat at high spatial resolutions to improve the ability to predict potential invasive species.